Using GitHub Enterprise Apps for Programmatic App Management Across Orgs
A comprehensive guide to using Enterprise GitHub Apps to programmatically install and manage applications across all organizations in your GitHub Enterprise
Overview
GitHub has made enterprise GitHub App management much easier with the general availability of Enterprise GitHub Apps and Enterprise-level access for GitHub Apps and installation automation APIs (public preview). These capabilities allow enterprise administrators to programmatically install, manage, and audit GitHub Apps across hundreds of organizations without manually clicking through installation screens. This is particularly useful during migration scenarios where you need to programmatically install and configure apps across multiple organizations.
This post shows how to use these new APIs with practical bash examples.
Check out my Demystifying GitHub Apps: Using GitHub Apps to Replace Service Accounts post if you’re interested in learning more about what a GitHub App is! 🚀
What Are Enterprise GitHub Apps?
With the March 2025 GA release of enterprise-owned GitHub Apps and the July 2025 introduction (public preview) of enterprise-level access and installation automation APIs, enterprises can now:
- Install GitHub Apps at the enterprise level with new enterprise-specific permissions
- You can now use an App to authenticate to some endpoints at the Enterprise level
- Previously, Apps could only be installed at org/user level without enterprise API access
- Note not all enterprise endpoints are available yet (see: limitations)
- Programmatically manage app installations across all organizations in their enterprise, such as:
- Adding or removing repositories (you could previously do this at the organization level with an API, but only with a classic PAT)
- Toggling from all repositories to selected (a feature that was previously not possible through any API)
- Automate GitHub Apps installation using the Enterprise-level REST APIs (it wasn’t possible to programmatically install an app before!)
- Centrally audit and control which apps are installed and what they can access
- Previously, if you wanted to get which repositories the app had access to, you had to use an App’s JWT token to query the installation and using the
repository_selectionproperty
- Previously, if you wanted to get which repositories the app had access to, you had to use an App’s JWT token to query the installation and using the
- Automatic permission propagation: When you update app permissions, all organizations automatically accept the changes without requiring manual approval from each org owner (huge for enterprises with many organizations!)
- Transfer existing organization apps: Organization-owned GitHub Apps can now be transferred to enterprise ownership, allowing you to centralize management of apps that were previously created at the organization level
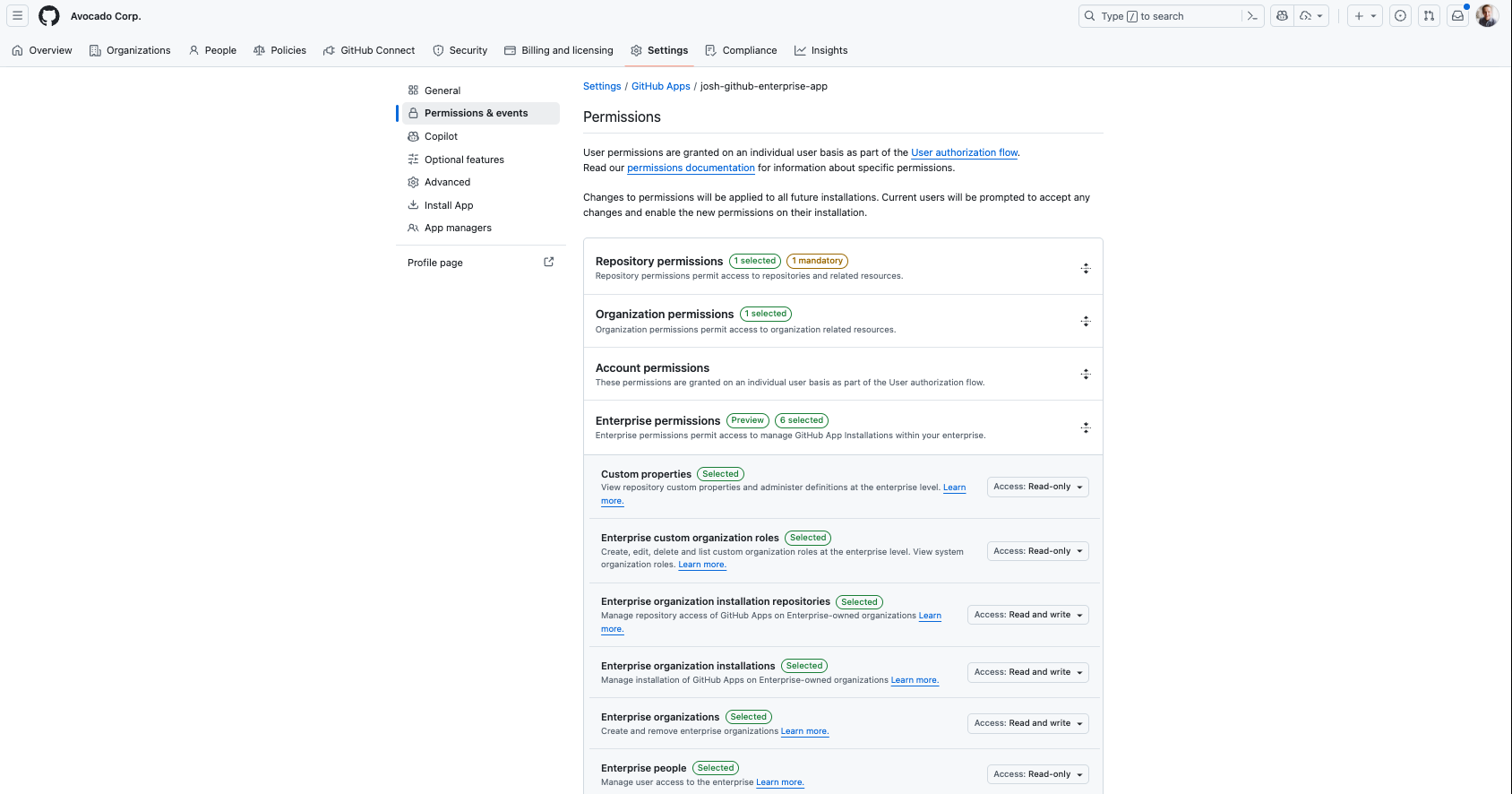
Enterprise App Permission Scopes & Capabilities
Here’s a list of the scopes available to an Enterprise GitHub App. In this post, we are specifically focusing on how these can be used to manage app installations across your enterprise organizations:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Enterprise App Installation
├── Enterprise-level permissions (new)
│ ├── Enterprise custom properties
│ ├── Enterprise custom organization roles
│ ├── ⭐️ Enterprise organization installation repositories
│ ├── ⭐️ Enterprise organization installations
│ ├── Enterprise organizations (create and removing enterprise orgs)
│ ├── Enterprise SSO and SCIM management
│ ├── Enterprise people (managing user access to the enterprise)
│ └── Enterprise single sign-on (view and manage SSO information; does not replace setup EMU user)
└── Organization App installations (Enterprise Apps can now manage)
├── Installing/uninstalling the app in an org
└── Repository access settings (flipping access between all repos to selected repos)
└── Repository access list (adding/removing repos the app has access to)
You can use an Enterprise-owned GitHub App to install another Enterprise-owned GitHub App into an organization, an organization-owned GitHub App, or even a third-party Marketplace app into an organization. The key difference is that the Enterprise-owned App has enterprise-level permissions and can be managed centrally by enterprise owners. See my post on installing Marketplace apps with Enterprise Apps for a walkthrough.
Installation Automation API Examples
Now that we understand what Enterprise GitHub Apps can do, let’s look at the automation APIs. These examples show how to manage app installations across your enterprise organizations programmatically.
Before diving into the examples, there are a few important things to know:
- Prerequisites: You’ll need enterprise owner access (or delegated app manager permissions), and an Enterprise GitHub App with Enterprise –> “Enterprise organization installations” (write) permissions (and generate and safeguard the private key).
- Authentication: In my examples, I’m using the
gh tokenCLI command to generate a token for App authentication. You can also generate your own JWT and App installation token using your preferred method. - API Documentation: There are two different sets of API endpoints for Apps, and navigating the documentation can be tricky. We’ll be using the REST API for managing organization GitHub App installations for Enterprise Administration, not the regular REST API endpoints for GitHub Apps (which are app and org-based, not enterprise).
Examples (Bash)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# Generate token for the enterprise app
# The --installation-id option can be omitted if the App's first installation was at the enterprise (no orgs)
# Find the installation ID from address bar when reviewing the app's installation configuration
token=$(gh token generate --app-id 1891481 --installation-id 84179086 --key /Users/joshjohanning/Downloads/josh-github-enterprise-app.2025-09-03.private-key.pem --token-only)
# Get repositories accessible to an app installed in org
# This effectively shows which repos the app is installed on
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/organizations/joshjohanning-org/installations/45357471/repositories --paginate --jq '.[].full_name'
# Get repositories belonging to an enterprise-owned organization
# Useful to know WHICH repos are available to install the app on
# or compare with the previous API to see which repos the app is NOT installed on
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/installable_organizations/joshjohanning-org/accessible_repositories --jq '.[].full_name' --paginate
# Flip to "selected repositories" for app installed in org
# Note this fails with `422` if you select invalid repos
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api --method PATCH /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/organizations/joshjohanning-org/installations/45357471/repositories --input - <<< '{
"repository_selection": "selected",
"repositories": [
"issueops-samples",
"reusable-workflows"
]
}'
# Flip back to "all repos" for app installed in org
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api --method PATCH /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/organizations/joshjohanning-org/installations/45357471/repositories --input - <<< '{
"repository_selection": "all"
}'
# Uninstall app in an org
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api --method DELETE /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/organizations/joshjohanning-org/installations/45357471
# You need to retrieve the client_id of the app being installed in order to install it
# The easiest way is to grab the app's client_id from the app's settings page
# Programmatically:
# - If the app is public, you can query the client_id with any authentication (including Enterprise GitHub App)
# - If the app is private, you can query the client_id using the API with your user token with the scopes:
# $ gh auth login -s read:enterprise or gh auth login -s read:org
# $ gh api /apps/josh-github-enterprise-app-disc --jq .client_id
# Install app in an org
# Note it needs client_id and not the app_id
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api --method POST /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/organizations/joshjohanning-org/installations -f 'client_id=Iv1.1051aca2d4910a24' -f 'repository_selection=all'
# List all apps and their permissions in an organization
GH_TOKEN=$token gh api /enterprises/avocado-corp/apps/organizations/joshjohanning-org/installations --paginate
Current Limitations
As of September 2025, there are some limitations to be aware of:
- Limited permission scope: Not every permission is available at the Enterprise level yet (like managing Enterprise settings)
- Enterprise webhooks: Enterprise installations cannot subscribe to webhooks yet
Third-party apps: Enterprises can only install apps owned by the enterprise or organizations within the enterprise– This works! You just need the app’sclient_id. See my post on installing Marketplace apps programmatically with Enterprise Apps for details.- Rate limits: Enterprise installations have their own 15,000 requests/hour budget - but note each installation still has its own rate limit
- Creating apps: You cannot currently create Apps through the API; I recommend using the manifest flow for codifying the app permissions and creation process through the UI
Keep an eye on the GitHub roadmap and changelog for updates on enterprise GitHub App capabilities.
Summary
Enterprise-owned GitHub Apps (GA March 2025) and the Enterprise-level installation automation APIs (public preview July 2025) solve the manual pain of managing apps across many organizations. The key benefit is eliminating the need to click through installation screens for every org, plus automatic permission propagation when you update app settings.
The bash examples above demonstrate the core operations: install, uninstall, change repository access, and audit existing installations. These Enterprise-level GitHub App management APIs are particularly valuable during migrations or when you need to deploy security/compliance apps enterprise-wide.
Happy automating! 🔑 🚀